Multimedia in the Web (M152)
Translated from German using DeepL.
Date: September 2022
Reading time: 8 minutes
In this blog post, I will show you what you should bear in mind when choosing the file format. I also go into the property rights and describe how developers can make use of them.
Last but not least, I explain what rules you should follow when taking the perfect photo and how to set up your camera accordingly.
We covered most of these topics at vocational school. Module 152 deals with topics relating to multimedia.
File formats
At the beginning of this module, we examined the various file formats. We realized that there are several options to choose from.
Often the familiar formats are simply used. However, if you invest a little time and weigh up the options, you can sometimes find a better solution.
Image
When choosing a file format for images, it is advisable to pay attention to these five areas.
Compression
With images, a distinction is made between lossless and lossy compression. If an image is compressed with lossless compression, every bit can be restored. After lossy compression, unnecessary information is eliminated. After enlarging the file, it is no longer in the same quality as it was before.

Source: https://gisgeography.com/ (opens in a new tab)
Vector
Vector graphics are mathematically defined images. These are saved on a raster. Such files can be scaled indefinitely. This is because the graphics are recalculated each time.
Such graphics are mostly used for logos or icons.
Another advantage is that programmers can easily change the colors of the images.
Vector graphics reach their limits when it comes to saving color gradients or shapes from nature.
Transparency
When deciding on the format, you should also always consider whether you want to crop certain parts. This is supported by the PNG, GIF and vector formats.
Color depth
The color depth describes how many colors can be saved. With GIF, for example, only 256 colors can be saved.
Browser compatibility
The format is only useful if it is supported by the browsers. Compatibility can be checked on this website: https://caniuse.com/ (opens in a new tab)
Audio
Sample rate
The sample rate determines the intervals at which a level change can be recorded. The higher this value is, the more accurately a sound can be recorded.
Resolution
The resolution specifies how much memory can be used for a level change. The more memory available, the greater the range over which a signal can be distributed.
Conclusion
My personal choice for ordinary images is usually PNG. However, as already described, this depends very much on the scenario.
In the audio sector, I am convinced by MP3 and WAV. These are the most common formats, which are also extremely compatible. WAV requires a little more memory, but offers better sound quality.
Tip for developers
There is a service where you can upload your images. This is called Cloudinary: https://cloudinary.com/ (opens in a new tab)
If you then need an image on a website, you send a request. The service recognizes the browser and delivers the image in the most suitable file format.
The desired resolution of the image can also be specified. This allows you to display smaller images in smaller viewports and thus improve performance.
The disadvantage is that you are dependent on Claudinary. A request also costs time.
Property rights
Property rights give the owner rights. They can exclude third parties from commercial use. This is how innovations become a tradable good.
- Rights expire after a period of protection
- Rights are only valid in a specific country
- Only commercial use is protected (as a rule)
There are different types of intellectual property rights. These are selected based on the innovation.
| Trademark protection | Patent protection | Design protection | Copyright | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| What | Registered characters | Inventions | Design of an object | Literature and art |
| How | Entry in the commercial register | Grant of the invention patent | Entry in the design register | Automatic |
| Duration | 10 years (can be extended as required) | max. 20 years | 5 years (4 x 5 years extendable) | up to 70 years after the death of the authorComputer software: up to 50 years after the death of the author |
| Fee | Registration: 550 CHFExtension: 550 CHF | Registration: 200 CHF(Research: 500 CHF)Audit: 500 CHFExtension:5th and 6th year: 100 CHF7th and 8th year: 200 CHFfrom 9th year: 310 CHF | Basic fee: 200 CHFExtension: 200 CHF (5 years) | None |
| Symbols (optional use) | Registered Trademarks: ®Trademark: ™ | +pat+ | mod. dép | © |
Copyright
For something to be protected by copyright, it must fulfill three criteria:
- Intellectual creation
- Literature and art
- Individual character
Since software falls under the category of copyright, I will go into more detail here.
Parts of copyright
Copyright can be divided into two parts.
Moral rights
These rights always belong to the creator.
- Publication rights
- Right to recognition
- Right to prohibit distortions
Rights of use and exploitation
These rights also belong to the creator. However, the creator can assign or sell them.
- Right of reproduction
- Right of distribution
- Right of making available
- Right of performance and presentation
- Right of adaptation
Alternative forms
Copyright law severely restricts the use of a work.
However, sometimes you want to make a work available. For this reason, there are alternative forms to copyright.
Creative Commons
With Creative Commons, you can make your work available to the world and still restrict its use in certain respects. You can obtain a Creative Commons license on the following website: https://creativecommons.org/choose/ (opens in a new tab)
To do this, you have to answer a few questions on the left. On the right-hand side you will then see the generated license.

This process is free of charge. The license can then be used officially. To attach the license, you can for example copy the HTML markup and then paste it on your website.
<a rel="license" href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/">
<img
alt="Creative Commons License Agreement"
style="border-width:0"
src="https://i.creativecommons.org/l/by-nc-nd/4.0/88x31.png"
/>
</a>
<br />
This work is licensed under a
<a rel="license" href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/">
Creative Commons Attribution - Non-commercial - No Derivatives 4.0
International License
</a>
.OpenSource
OpenSource means that other people are allowed to view, study and modify the source code. The aim is usually to enable a community to further develop the software.
Copyleft
In an OpenSource project, as already described, the entire code may be copied. Now a company could use this code to create and market a paid product. Copyleft prohibits exactly this. Copyleft works may be copied and modified. However, all resulting methods must also be returned to the open source community.
Licensing a Git repository
In class, we did not deal with the topic of how to license a Git repository. However, I think this is still an important topic. For this reason, I looked up what the typical procedure is.
Projects in a Git repository are of course also protected by copyright. So if there is no license in a project, no one is allowed to use the code.
If you want to give up more rights, you can do so with the help of a license. This can be obtained via the following page, for example: https://choosealicense.com/ (opens in a new tab)

Now select the appropriate license.

You can see directly which permissions, conditions and limitations are associated with the license.
If you are satisfied with the license, copy the text and paste it into the root of the project. It is best to do this in a LICENSE.txt, LICENSE.md or LICENSE.rst file.
Image compositions
Format
First of all, you have to decide in which format you want to capture a moment. A distinction is made between portrait and landscape format. (Portrait and Landscape in English) The choice of format depends on the subject and the mood you want to convey. Portraits are taken in portrait format. Landscapes are usually photographed in landscape format.
Golden ratio
Source: https://www.toushenne.de/files/robertweller/img/2018/goldene-spirale.png (opens in a new tab)
The golden ratio is a rule. It describes the division ratio of a distance. People perceive this ratio as harmonious.
The golden ratio can be found in nature, art, architecture and design.
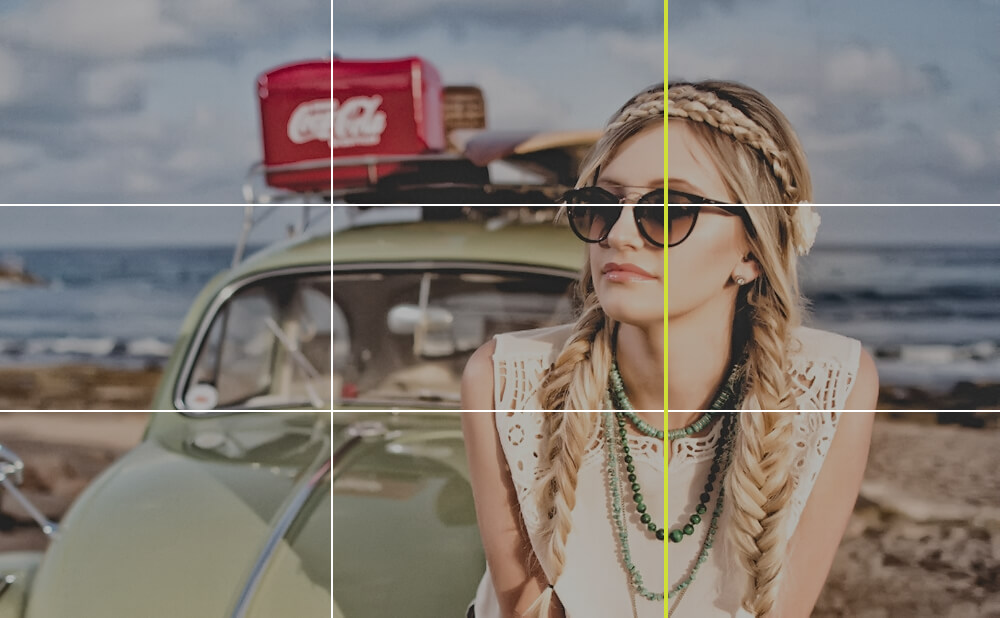
Rule of thirds
In photography, it is not possible to photograph the subject perfectly in the golden ratio. That is why this rule was created. To apply it, you divide an image into nine fields. Cameras and cell phones almost always have the option of displaying this grid. The rule states that the subject should be on the right-hand vertical line. In the best case, the most important point is on the intersection point at the top right.

Horizontal
There are three basic ways to convey a mood in photos with a horizon.
A low horizon symbolizes freedom and is often used when either a beautiful horizon or a slightly more boring ground is visible.
With a high horizon, you can depict the many details of the ground.
The horizon is rarely placed in the center of the picture. However, if you want to achieve a mirror effect (with water), this method can serve its purpose.
Camera settings
We have not yet taken any photos in this module. However, we have already dealt with the basic camera settings.

Aperture
The smaller the aperture, the sharper the background of the image. However, the image also becomes darker.
Exposure time
If you select a shorter exposure time, you can capture more movement. However, this also results in a darker image.
ISO
The ISO value should normally be left at a low sensitivity.
If the image is too dark, you can increase this value. However, this will result in a somewhat grainy image.
Brightness
In my opinion, the biggest difficulty is adjusting the brightness of the image. You always have to find the perfect compromise.
Example:
A sports photographer attends a football match and wants to take a few pictures. As the players are often in motion, he has to choose a shorter exposure time. This allows him to capture the movements. The problem, however, is that the picture becomes a little dark. Now he can choose a larger aperture, for example. This makes the picture brighter again. But the background is blurred.
He could also opt for a medium aperture and brighten the image with a higher ISO sensitivity. However, the image may be too grainy this way.
To practise using these values, I recommend the following website: http://canonoutsideofauto.ca/play/
Conclusion
So far, I really like this module. It also shows us computer scientists which tools and file formats the designers work with.
Over the next few weeks, we'll be looking at logos, videos and responsiveness. I'm also excited to see what else I can learn.
I think this module gives you a good insight into important topics. I'm just a little surprised that this subject is only taught in the fourth year of the apprenticeship.